Manufacturing Of Bricks
- The manufacturing process of bricks consists of 4 operations:
(1) Preparation of brick clay or brick earth
(2) Moulding of bricks
(3) Air drying of bricks
(4) Burning of bricks
1. Preparation of Brick Earth
(i)Unsoiling
(ii) Digging
(iii) Cleaning
(iv)Weathering
(V) Blending
(vi) Tempering.
(i) Unsoiling: Top layer of soil about 200 mm in depth is taken out and thrown away as it contains impurities
(ii) Digging: Clay is dug out and spread on the levelled ground.
(iii) Cleaning: Clay should be free from stones, pebbles, vegetable matter, etc. If these particles are in excess, the clay is to be washed and screened.
(iv) Weathering: Clay is then exposed to the atmosphere for softening or mellowing, period of exposure varies from few weeks to full season.
(v) Blending: Clay is made loose and any ingredient to be added to it is spread out at its top. It is carried out by taking a small portion of clay every time and by turning it up and down in a vertical direction.
(vi) Tempering: Water in required quantity is added to clay and the whole mass is kneaded or pressed under the feet of men or cattle. To obtain a homogeneous mass having uniform character.
- For manufacturing good brick, tempering is done in pug mills and operation is called pugging. In pug mill, feeding of clay from top and taking out of pugged clay from bottom are done simultaneously.
2. Moulding
It is the process of filling the prepared clay into moulds of definite size and pattern. It can be done using hand moulding or machine moulding technique.
- This method is adopted when manpower is cheap and is easily available for manufacturing bricks, usually done on small scale.
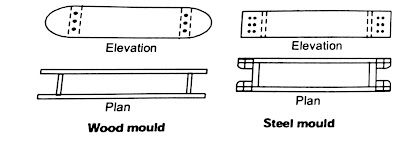
- Moulds are rectangular boxes of wood or steel, open at the top and bottom.
- This method is adopted when a large and level land is available. In this process, the ground is levelled and sand is sprinkled over it. Now mould is lifted and raw brick is left on the ground.
- Mould is dipped in water and placed over the ground and then clay is pressed in the mould such that it fills all the corners.
- Extra or surplus clay is removed either by a wooden strike or metal strike. A strike is a piece of wood or metal with a sharp edge.
- Now mould is lifted and raw brick is left on the ground.
- To prevent the moulded bricks from sticking to the side of the mould, sand is sprinkled on the inner sides of the mould, or the mould may be dipped in water every time before moulding is done.
- If sand is sprinkled then bricks are called sand-moulded bricks, whereas in the case of mould dipped in water bricks are called slop-moulded bricks.
- Sand moulded bricks are better since they provide sufficient rough surface necessary for achieving a good bond between bricks and mortar.
- Ground-moulded bricks of better quality and with frogs on their surface are made by using a pair of pallet boards and a wooden block.
- The process of moulding these bricks is just similar to the above. But in this case, the moulder stands near a table of size about 2 x 1m.
- Clay, mould, water pots, stock board, strikes and pallet boards are placed on this table.
- Bricks are moulded on the table and sent for the further process of drying.
- Here efficiency of the moulder decreases gradually because of starding at the same place for a long time and thus Cost of brick moulding increases.
- Moulding is done with the help of machines when bricks are required in a large quantity in a short span of time.
- It is helpful for moulding hard and strong clay.
- Machine moulding can further be classified into two ways. (a) Plastic Clay Machine and (b) Dry Clay Machine
- In this method pugged, stiffer clay is forced through a rectangular opening of brick width) size by means of an auger.
- These bricks come out of the opening in the form of a bar and further these bricks are cut into strips thickness (dimensions equal to the brick) by wires fixed in frames.
- In these machines, the strong clay is first converted into powder form. A small quantity of water is added to form a stiff plastic paste. Such paste is placed in a mould and pressed to form bricks. These bricks do not practically require drying. They can be sent directly for the process of burning.
- Such pressed bricks are more dense, smooth and uniform than ordinary bricks.
- These are burnt carefully as they are likely to crack.
- If Green bricks containing 7-30% moisture burnt, then it is likely to be cracked and distorted.
- Therefore moulded bricks are dried first to remove moisture for controlling shrinkage and saving of fuel during burning.
- It is a normal practice to dry moulded bricks to approximate moisture content of 5-7%. The drying period usually varies from 7-14 days.